Design Process
User Centred Design (UCD)
Principles
- Understand users' needs - build a product that meets real needs
- Design the UI first - design the UI first, then design the architecture to support that UI
- Iterate - a great design requires iterations
- Use it yourself - find problems that can be fixed while it's still easy to fix
Observe others using it - observe other people using your UI in a realistic way very early in the development cycle
Storyboard is a quick way to sketch out sequence and schematics
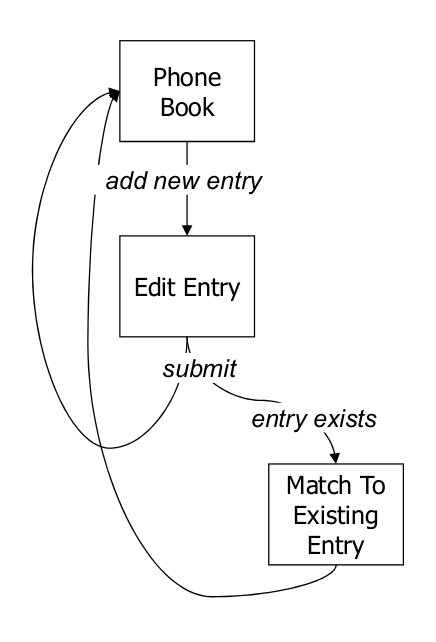
Interaction Sequences
- Convey the big pricture of system interaction
- Interaction paths (flow chart)
- Focus on interface logic
Interface Schematics
- Microstructure
- Convey essential content and functionality at individual steps of interaction
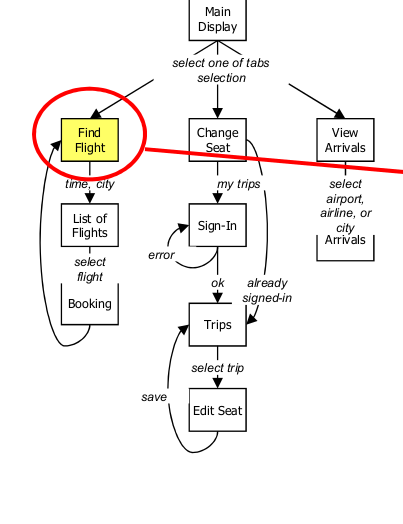
Interface Schematics
- Also referred to as wireframing
- Has enough detail so that someone could begin designing and implementing system logic
- Different than graphic design mockup or paper prototypes
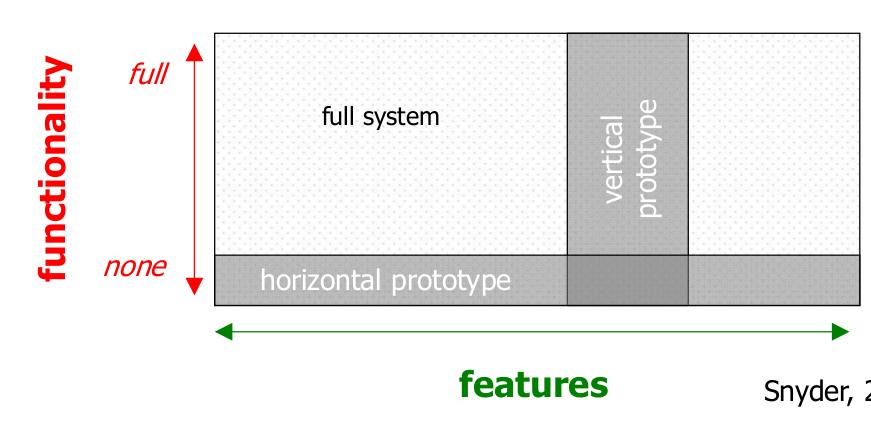
Prototypes
- A limited representation of a design that allows people to interact with it and to explore its suitability
- e.g. paper sketches, slide show, software/hardware with limited functionality
Fidelity
- Faithfulness of prototype appearance and performance to final product
| Low | High |
|---|---|
| Easy and fast to implement | False sense of completeness |
| More creative | More accurate |
Wizard-of-Oz Technique (WoZ)
- Evaluate unimplemented technology by using a human to simulate the response of the system
Breadth vs. Depth
- Breadth refers to the amount of features in the system
- Depth refers to the amount of interactivity and functionality of the system