Ogliopoly
- Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms
- A small number of firms compete
- Dualpoly - a market with two firms (e.g. AMD and Intel)
- Cartel - a group of firms in collusive agreement
- Temptation to form one
- Mostly illegal
- Interdependence of profits
Game Theory
- A tool for studying strategic behaviour
- Behaviour that takes into account the expected behaviour of others and the mutual recognition of interdependence
Rules
- Describe the setting of the game, the action the players may take, and the consequences of those actions
Strategies
- All the possible actions of each player
Payoffs
- Profits and losses of player
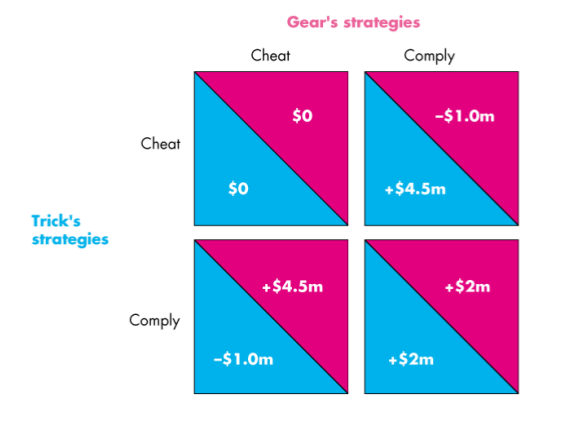
- A payoff matrix shows payoffs for every possible action by each player
Outcome
- Determined by players' choices
Nash equilirium
- A takes the best possible action given B's action
- B takes best possible action given A's action
Collusion
- A collusive agreement is an agreement between two (or more) firms to restrict output, raise the price, and increase profits
- Mostly illegal
- Firms in a collusive agreement operate a cartel
Strategies
- Comply (e.g. increase output)
- Cheat
One comply, one cheat
- The complier incurs economic loss, the cheat increases economic profit
Both cheat
- Produces a competitive outcome
Tit-for-tat strategy - taking the same action the other player took last period (lightest punishment)
Trigger strategy - cooperating until the other player cheats, then cheating forever (most severe punishment)
- In a contestable market there are few firms but free entry and exit, so existing firms face competition from potential entrants
Payoff Matrix