Monopolistic Competition
- A large number of firms compete
- Each firm produces a differentiated product
- Firms compete on product quality, price and marketing
- Firms are free to enter and exit the industry
Product Differentiation
- When the firm makes a product that is slightly different from the products of competing firms
Entry and Exit
- There are no barriers to entry
- Firm cannot make an economic profit in the long run
Price and Output
- The firm in monopolistic competition operates like a single-price monopoly
- The firm produces the quantity at which MR=MC and sells that quantity for the highest possible price
- It makes an economic profit when P>ATC
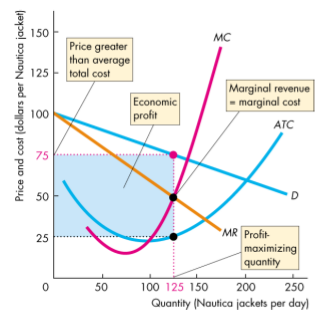
- Long run economic profit =0,P=ATC
Compared to Perfect Competition
- Excess capacity - if a firm produces less than the quantity at which ATC is a minimum
- Markup - the amount by which its price exceeds its marginal cost
- Firms operate with excess capcity in long-run equilibrium
- Produce less than the efficient scale - the quantity at which ATC is a minimum
- Doward sloping demand curve
- Firms operate with positive markup
- Result of the downward sloping demand curve
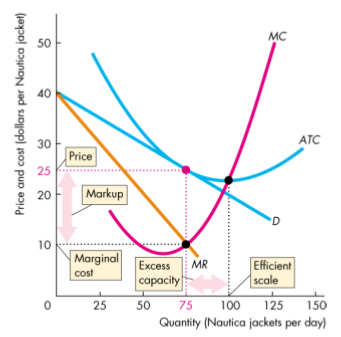
- Firms in perfect competition have no exccess capacity and no markup
- Result of the perfectly elastic demand curve
Product Development and Marketing
- Firms must continously innovate and develop new products
- New firms enter similar products compete away economic profits
Advertising
- Increase costs
- Signal quality - send a message to uninformed people
- Create perception of product differentiation even when th actual product differences are small

