Final Study Notes
Elasticities
Price Elasticity of Demand
- Tests the elasticity of a good
- Perfectly elastic
- Elastic
- Inelastic
- Perfectly Inelastic
- Elastic - 1% decrease in price increases quantity sold by more than 1%, total revenue increases
- Inelastic - 1% decrease in price increases quantity sold by less than 1%, total revenue decreases
- Unit Elastic - nothing happens
Cross Elasticity of Demand
- Tests the relationship of two goods
- Substitutes
- Indenpendent
- Complements
Income Elasticity of Demand
- Tests the type of the good
- elastic (normal good)
- inelastic (normal good)
- negative elasticity (inferior good)
Elasticity of Supply
- perfectly elastic (horizontal)
- elastic
- unit elastic
- inelastic
- perfectly elastic (vertical)
Budget Equation
- Assume we have the goods Pop and Movies
- Income
- The real income in terms of the quantity of the goods are the intercepts
Marginal Rate of Substitution
- Utility maximization
- marginal utility of good
Indifference Curves
Shapes of Indifference Curves
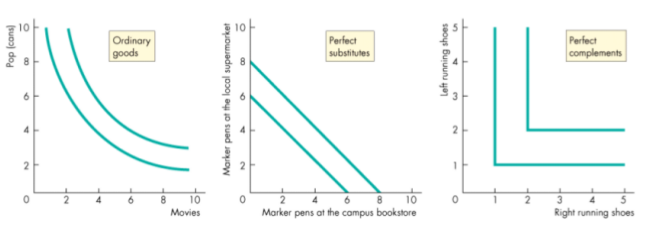
Measuring the Substitution Effect
- Take the new budget line (generated from price change)
- Move it in parallel until it hits the original indifference curve
- The movement between the tagent of the initial tangent on the initial indifference curve to the new tagent on the same curve is the substituion effect
Measuring the Income Effect
- Consider the shifted budget line
- Move it in parallel to the initial indifference curve
- The movement from the tangent of the new budget line on the initial indifference curve to the tagent of the new budget line on the shifted the indifference curve is the income effect
Output and Costs
- AP rising
- AP falling
- Max AP
Short Run Equilibrium Cost
Perfect Competition
AR = Average revenue MR = Marginal revenue P = Price
- Economic profit is maximized at the quantity where
- Shutdown point is at minimum AVC