Monopoly
Barriers to Entry
- A contraint that protects a firm from potential competitors
Natural
- A market in which economies of scale enable one firm to supply the entire market at the lowest possible cost
Ownership
- If one firm owns a significant portion of a key resource
Legal
- Competition are restricted by granting of a public franchise, government license, or patent/copyright
Price Setting Strategies
- A monopoly is a price setter since the demand for the monoply's output is the market demand
Single-price monopoly
- A firm that must sell each unit of its output for the same priec to all its customers
- Marginal revenue - the change in total revenue that results from a one-unit increase in the quantity sold
- For a single price monopoly, marginal revenue is less than price at each level of output
Compared to Competition
- Single-price monopoly competitive
- Single-price monopoly competitive
Marginal Revenue Curve

- Marginal revenue is related to the elasticity of demand of it's good
- If elastic, the fall in price brings an increase in total revenue
- If ineasltic, a fall in price brings a decrease in total revnue

- Never produces an output at which demand is inelastic
- Since a firm can increase economic profit by decreasing output if it producing such an output
ATC Curve
- Tells us the average total cost
- Economic profit is the profit per unit multiplied by the quantity produced (blue triangle)
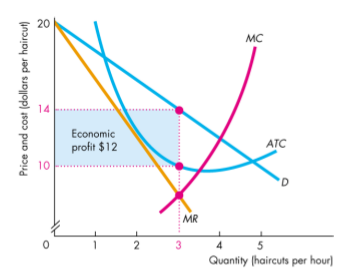
Maximizing Profit
Selects the profit-maximizing quantity in the same manner as a competitive firm
- Also referred to as
Equilibrium price occurs on the demand curve at the profit maximizing quatity
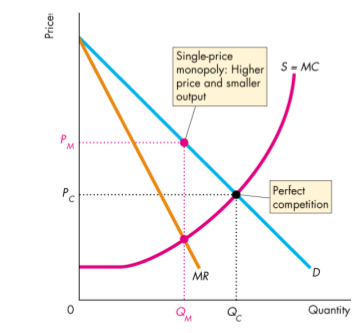
Total Surplus

- The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized
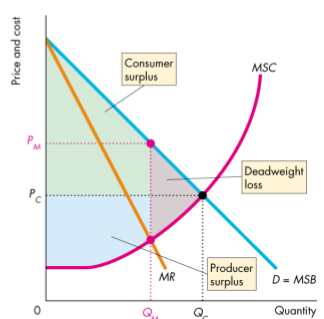
Inefficiency of monopoly
- Price exceeds marginal social cost, marginal social benefit exceeds marginal social cost
- Deadweight loss arises
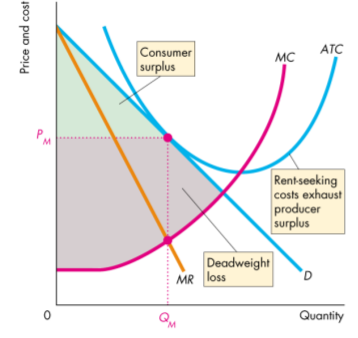
Rent Seeking
- Any surplus (consumer, producer, economic profit) is called economic rent
- Rent seeking - is the pursuit of wealth by capturing economic rent
- Buy a monopoly
- Create a monoply
- Rent-seeking equilibrium - the resources used in rent seeking can exhaust the monopoly's economic profit and the monopoly breaks even
Other facts
Faces the same types of technology constraints as competitive firm
Might make an economic profit in the long run since the barrier protects the firm from market entry by competitor forms
Might shutdown temporarily in the short run or exit the market in the long run if it incurs an econimic loss
Price discrimination
- The practice of selling different units of a good or service for different prices
- Does not have to be monopoly firms
Can descriminate among
- Among a group of buyers (airline tickets)
- Among units of a good (quantity discounts)
Product cannot be resold
- Increase the firm's profit by converting consumer surplus into economic profit
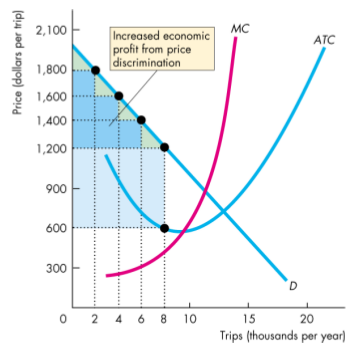
- Perfect price descrimination - if a firm is able to sell each unit of output for the highest price anyone is willing to pay
- Marginal revenue equals the price; demand curve is the marginal revenue curve
- The profit maximizing output increases to the quantity at which price equals marginal cost
- Economic profit increases above that of a single-price monopoly
- Deadweight loss is eliminated
Efficiency and Rent Seeking
- The more perfectly a monopoly can price discriminate, the closer its output is to the competitve output () and the more efficient is the outcome
- Different from the outcome of perfect competition
- The monopoly captures the entire consumer surplus
- The increase in economic profit attracts even more rent-seekinga ctivity that leads to inefficiency
Monopoly Regulation
Regulation - rules administrated by a government agency to influence prices, quantities, entry, and other aspects of economic activity
Social interest theory - the political and regulartory process relentlessly seeks out inefficiency and regulates to eliminate deadweight loss
Public Choice theory - people in government (elected or employed) respond to incentives, they attempt to advance their own self interest
Capture theory - predicts regulations serve self-interest of producers, who "capture" the regulator
Efficient Regulation of a Natural Monopoly
- Regulate natural monopoly so that it produces the efficient quantity
- Marginal cost pricing rule - a regulation that sets the price equal to the monopoly's marginal cost
- The quantity demanded at a price equal to marginal cost is the efficient quantity
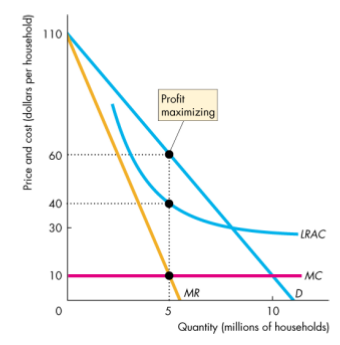
Unregulated
- Maximizes economic profit by producing the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
- Charging the highest price at which that quantity will be bought
Regulated
- Demand curve is the MSB curve
- Marginal cost curve is the MSC curve
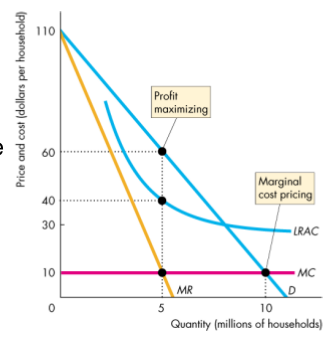
- The quantity produced is efficient
- May suffer economic loss when the average cost exceeds the price
- May be permitted to price discriminate to cover the loss from marginal cost pricing
- Charge a one-time fee to cover its fixed lost and then charge a price equal to marginal cost
- An alternative would be produce the quantity at which price equals to average cost and to set the price equal to average cost - the average cost pricing rule
The government may also pay a subsidy equal to the monopoly's loss
Rate of return regulation - set a price to acheive target rate of return on capital
- Price cap regulation - set price ceiling to achieve target rate of return on capital