Perfect Competition
The Firm's Output Decision
- A perfectly competitive firm chooses the output that maximizes it's economic profit
- We can determine the profit-maximizing output by looking at the firm's total revenue and total cost curves
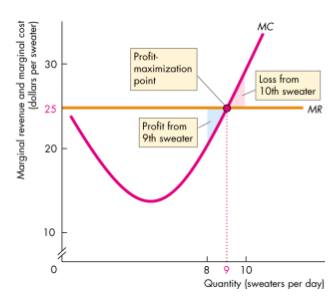
- If economic profit increases if output increases
- If economic profit decreases if output increases
- If economic profit decreases if output changes; profit maximized
Temporary Shutdown Decision
- When taking economic loss, a firm must decide whether to exit or stay in the market
- If the firm stays in the market, if must dcide whether to produce something or shut down temporarily
- The decsion will be the one that minimizes the firm's loss
Calculating economic loss:
TFC - Total fixed cost
TVC - total variable cost
TR - total revenue
- If the firm shuts down, Q is 0 and the firm still has to pay it's TFC
The Shutdown Point
- When it is indifferent between producing and shutting down
- When AVC is at it minimum
- Also the point at which the MC curve crosses the AVC curve
- The firm incurs a loss equal to TFC from either action
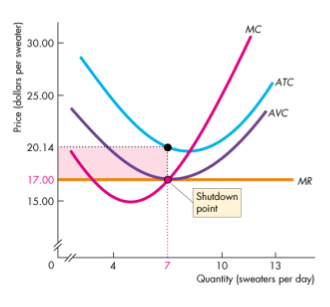
- The firm incurs a loss equal to the red rectangle
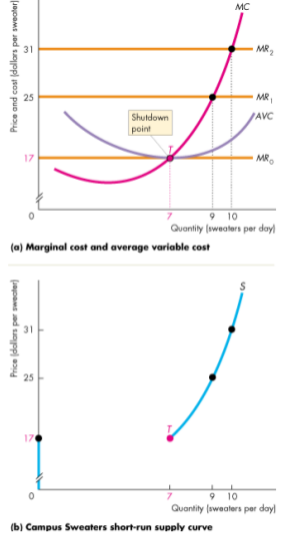
The Firm's Supply Curve
- A perfectly competitive firm's supply curve shows how the firm's profit-maximizing output varies as the market price varies, other things remain the same
- Linked to the marginal cost cruve
- Produces nothing below the shutdown point
The Firm's Demand Curve
- Perfectly elastic (0 slope)
- Equals to the firm's marginal revenue curve
Entry and Exit
- New firm enters an industry in which existing firms make an economic profit
Firms exit an industry in which they incur an economic lossb
When new firms enters the market, the market supply increases and the market price falls
In the long run, the price falls until firms are making zero economic profit
When firms exit the market, the market supply decreases and the market price rises
In the long run, the price continues to rise until firms make zero economic profit
Techonological Change
- New technologies that lowers costs and constantly being discovered
- Allows a firm to produce at lower average cost and marginal cost
- Cost curve shift downward
- Firms that adopt the new technology mak an economic profit
- New techonology firm enter and old technology firms either exit or adopt the new technologies
- Industry supply increases and the industry supply curve shifts rightward
- This continues until a new long-run equilibrium emerges in which all firms use the new technologies, the price equals minimum average cost, and each firm makes zero economic profit