Output and Costs
Short-Run Cost
- To produce more output in the short run, the firm must employ more labour, which means that it must increase its costs
Total cost (TC)
- The cost of all resources used
Total fixed cost (TF)
- The cost of the firm's fixed inputs
- Do not change with output
Total variable cost (TVC)
- The cost of the firm's variable inputs
- Change with the outout
Relationship:
Total cost curves

Marginal Cost (MC)
- The increase in total cost that results from a one-unit increase in total product
- Increasing marginal returns => marginal cost falls as output increases
- diminishing marginal returns => marginal cost rises as output increases
Average fixed cost (ACF)
- Total fixed cost per unit of output
Average variable cost (AVC)
- Total variable cost per unit of output
Average total cost (ATC)
- Total cost per unit of output
Relationship:
Cost Curves and Product Curves
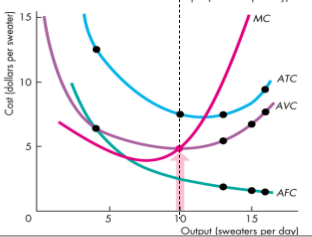
- The shape of a firm's cost curves are determined by the technology it uses
- By the shape of the total product curve
- MC _is at its minimum at the same output level at which _MP is at its maximum
- When MP is rising, MC is falling
- AVC is at its minimum at the same output level at which AP is at its maximum
When AP is rising, AVC is falling
The AVC curve is U-shaped because
- Initially MP exceeds AP, which brings rising AP and falling AVC
- Eventually MP falls below AP, which brings falling AP and AVC
The ATC curve is U-shaped for the same reasons
- The ATC falls at low output levels because AFC is falling quickly
- ATC curve is the vertical sum of the AFC curve and the AVC curve
- Influence of two opssing forces
- Spreading total fixed cost over a larger output - AFC curve slopes downward as output increases
- Eventually diminishing returns - the AVC curve slopes upwards and AVC increases more quickly than AFC is decreasing
Shifts in the cost curves
- The position of a firm's cost cruves depend on techonlogy and prices of factors of production
Technology
- Influences both the product curves and the cost curves
- Increase in productivity shifts the product curves upward and the cost curves downward
- If the technological advance results in the firm using more capital and less labour, fixed costs increase and variable cost decrease
- Average total cost increase at low output levels and decreases at output levels
Prices
- Increase in the price of a factor of production increases costs and shifts the cost curves
- Increase in a fixed cost shifts the TC and ATC upwards but does not shift the MC curve
- Increase in a variable cost shifts the TC, ATC, and MC curves upward
Long-Run Cost
- All inputs are variable and all costs are variable
- Depends upon on the firm's product function - the relationship between the maximum output attainable and the quantitiesof both capital and labour
Diminishing Marginal Product of Capital
Marginal product of capital - the increase in output resulting from a one-unit increase in the amount of capital employed, holding constant the amount of labour employed
- A firm's production function exhibits diminishing marginal returns to labour (for a given plant) and diminishing marginal returns to capital (for a quantity of labour)
- Creates a set of short run, U-shaped cost curves for MC, AVC, and ATC
Short and Long-Run Cost
- The larger the plant, the greater it the output at which ATC is at a minimum
- Each plant has a short-run ATC curve
- The firm can compare the ATC for each output at different plants
Long-Run Cost
- Made up from the lowest ATC for each output level
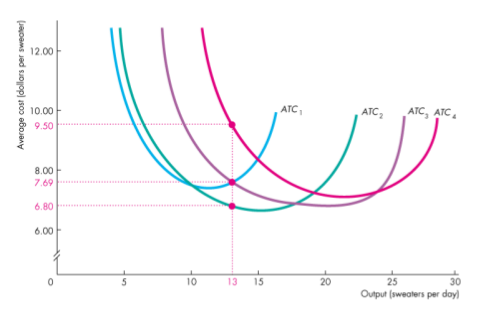
- By comparing the curves using differnet numbers of knit machines, we can see that the least-cost way of producing 13 sweater a day is to use 2 knitting machines ()
Long-run average cost curve - the relationship between the lowest attainable average total cost and output when both the plant and the labour are varied
- A planning curve that tells the firm the plant that minimizes the cost of producing a given output range
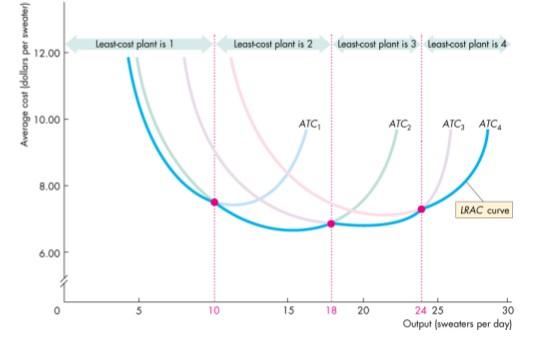
Economies and Diseconomies of Scale
Economies of scale - falling long-run average cost as output increases (e.g. technology)
Diseconomies of scale - rising long-run average cost as output increases
Constant returns to scale - constnat long-rn average costs as output increases
Minimum Efficient Scale
- The smallest quantity of output at which the long-run average cost reaches its lowest level
- If the long-run average cost curve is U-shaped, the minimum point identifies the minimum scale output level